What are the Signs and Symptoms of Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a silent disease. Because osteoporosis develops over the years, you may not be aware you have it until you break a bone. Learn the sign & symptoms of osteoporosis.
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle — so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses such as bending over or coughing can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures most commonly occur in the hip, wrist or spine.
Bone is living tissue that is constantly being broken down and replaced. Osteoporosis occurs when the creation of new bone doesn't keep up with the loss of old bone.
Osteoporosis affects men and women of all races. But white and Asian women — especially older women who are past menopause — are at highest risk. Medications, healthy diet and weight-bearing exercise can help prevent bone loss or strengthen already weak bones.
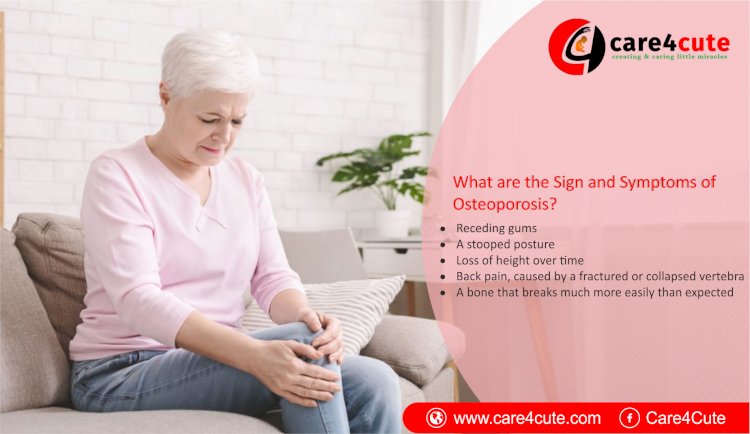
Signs and Symptoms of Osteoporosis
There typically are no symptoms in the early stages of bone loss. But once your bones have been weakened by osteoporosis, you might have signs and symptoms that include:
- Back pain, caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped posture
- A bone that breaks much more easily than expected
- Receding gums
- Decreased grip strength,
- Brittle bones,
- Decline in general fitness
Risk factors
A number of factors can increase the likelihood that you'll develop osteoporosis — including your age, race, lifestyle choices, and medical conditions and treatments.
Unchangeable risks
Some risk factors for osteoporosis are out of your control, including:
- Your sex. Women are much more likely to develop osteoporosis than are men.
- Age. The older you get, the greater your risk of osteoporosis.
- Race. You're at greatest risk of osteoporosis if you're white or of Asian descent.
- Family history. Having a parent or sibling with osteoporosis puts you at greater risk, especially if your mother or father fractured a hip.
- Body frame size. Men and women who have small body frames tend to have a higher risk because they might have less bone mass to draw from as they age.
Some other risk factors that contribute to osteoporosis are:
- Hormonal changes or menopause due to a drop in estrogen in women, and testosterone in men,
- Smoking
- Low calcium intake,
- Excessive caffeine or alcohol use
- Low level of Vitamin D,
- Low body mass,
- Hereditary conditions
Medical conditions
The risk of osteoporosis is higher in people who have certain medical problems, including:
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Kidney or liver disease
- Cancer
- Lupus
- Multiple myeloma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Prevention for Osteoporosis
Good nutrition and regular exercise are essential for keeping your bones healthy throughout your life.
Protein
Protein is one of the building blocks of bone. However, there's conflicting evidence about the impact of protein intake on bone density.
Most people get plenty of protein in their diets, but some do not. Vegetarians and vegans can get enough protein in the diet if they intentionally seek suitable sources, such as soy, nuts, legumes, seeds for vegans and vegetarians, and dairy and eggs for vegetarians.
Body weight
Being underweight increases the chance of bone loss and fractures. Excess weight is now known to increase the risk of fractures in your arm and wrist. As such, maintaining an appropriate body weight is good for bones just as it is for health in general.
Also Read - What Exercise should be Avoided in Osteoporosis?
Calcium
Men and women between the ages of 18 and 50 need 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day. This daily amount increases to 1,200 milligrams when women turn 50 and men turn 70.
Good sources of calcium include:
- Low-fat dairy products
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Canned salmon or sardines with bones
- Soy products, such as tofu
- Calcium-fortified cereals and orange juice
Exercise
Exercise can help you build strong bones and slow bone loss. Exercise will benefit your bones no matter when you start, but you'll gain the most benefits if you start exercising regularly when you're young and continue to exercise throughout your life.





































Comments (0)